Spring Boot Maven Plugin
Spring Boot Maven Plugin
定制layers.xml
packaging.layers.configuration
通过构建定制layers.xml文件,可以控制打包后的jar文件中的内容,从而实现更细粒度的控制。结合spring-boot-maven-plugin,可以实现在打包时将不同类型的文件放置在不同的层中,配合SpringBoot efficient-images从而实现更高效的部署和管理。
<!-- POM.xml -->
<build>
<finalName>${project.artifactId}</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot.version}</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>repackage</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
<configuration>
<layers>
<enabled>true</enabled>
<configuration>${basedir}/src/main/resources/layers.xml</configuration>
</layers>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<layers xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/boot/layers"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/boot/layers
https://www.springframework.org/schema/boot/layers/layers-3.2.xsd">
<!--application表示class和resource-->
<application>
<into layer="spring-boot-loader">
<include>org/springframework/boot/loader/**</include>
</into>
<into layer="application"/>
</application>
<!--dependencies所有依赖-->
<dependencies>
<!--<into layer="application">
<includeModuleDependencies/>
</into>-->
<into layer="snapshot-dependencies">
<include>*:*:*SNAPSHOT</include>
</into>
<into layer="module-dependencies">
<includeModuleDependencies/>
</into>
<!--<into layer="module-dependencies">
<include>com.ruoyi:ruoyi-*:*</include>
</into>-->
<into layer="third-dependencies"/>
</dependencies>
<!--定义层顺序,会影响BOOT-INF/layers.idx-->
<layerOrder>
<!--这里到顺序会影响直接通过java -jar xxx.jar方式启动时的类加载顺序,而docker分层优化部署时的顺序不受影响。-->
<layer>application</layer>
<!--模块依赖-->
<layer>module-dependencies</layer>
<layer>third-dependencies</layer>
<layer>spring-boot-loader</layer>
<layer>snapshot-dependencies</layer>
</layerOrder>
</layers>
classpath.idx
这是一个类路径索引文件,它包含了在构建过程中使用的所有类和资源的列表。这个文件通常由Maven插件生成,并包含在构建的JAR文件中。
官方解释:类路径索引文件可在 BOOT-INF/classpath.idx 中提供。通常,该文件由 Spring Boot 的 Maven 和 Gradle 构建插件自动生成。它提供了一个 jar 名称(包括目录)列表,并按照顺序将它们添加到 classpath 中。由构建插件生成时,该 classpath 排序与构建系统在运行和测试应用程序时使用的顺序一致。每行必须以破折号空格("--")开始,名称必须使用双引号。
该文件控制了类加载器的行为,它决定了类加载器在加载类和资源时的顺序。这个文件对于Spring Boot应用程序来说非常重要,因为它可以确保应用程序在运行时能够正确地加载类和资源。
过程分析
通过调试插件运行过程,可以发现:
- 在执行repackage方法时,会调用getLibraries方法,该方法会获取所有的库文件,并生成classpath.idx文件。相关代码如下:
// Packager
private void write(JarFile sourceJar, AbstractJarWriter writer, PackagedLibraries libraries) throws IOException {
if (isLayered()) {
writer.useLayers(this.layers, this.layersIndex);
}
writer.writeManifest(buildManifest(sourceJar));
writeLoaderClasses(writer);
writer.writeEntries(sourceJar, getEntityTransformer(), libraries.getUnpackHandler(),
libraries.getLibraryLookup());
Map<String, Library> writtenLibraries = libraries.write(writer);
writeNativeImageArgFile(writer, sourceJar, writtenLibraries);
if (isLayered()) {
writeLayerIndex(writer);
}
writeSignatureFileIfNecessary(writtenLibraries, writer);
}
Map<String, Library> write(AbstractJarWriter writer) throws IOException {
Map<String, Library> writtenLibraries = new LinkedHashMap<>();
for (Entry<String, Library> entry : this.libraries.entrySet()) {
String path = entry.getKey();
Library library = entry.getValue();
if (library.isIncluded()) {
String location = path.substring(0, path.lastIndexOf('/') + 1);
writer.writeNestedLibrary(location, library);
writtenLibraries.put(path, library);
}
}
// 写入classpath.idx
writeClasspathIndexIfNecessary(writtenLibraries.keySet(), getLayout(), writer);
return writtenLibraries;
}
- classpath.idx内容最初来自于maven生成的project对象中,相关代码如下:
// RepackageMojo
private void repackage() throws MojoExecutionException {
Artifact source = getSourceArtifact(this.classifier);
File target = getTargetFile(this.finalName, this.classifier, this.outputDirectory);
Repackager repackager = getRepackager(source.getFile());
// 获取所有的库文件
Libraries libraries = getLibraries(this.requiresUnpack);
try {
LaunchScript launchScript = getLaunchScript();
repackager.repackage(target, libraries, launchScript, parseOutputTimestamp());
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new MojoExecutionException(ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
updateArtifact(source, target, repackager.getBackupFile());
}
protected final Libraries getLibraries(Collection<Dependency> unpacks) throws MojoExecutionException {
Set<Artifact> artifacts = this.project.getArtifacts();
Set<Artifact> includedArtifacts = filterDependencies(artifacts, getAdditionalFilters());
return new ArtifactsLibraries(artifacts, includedArtifacts, this.session.getProjects(), unpacks, getLog());
}
// MavenProject
public Set<Artifact> getArtifacts() {
if (artifacts == null) {
if (artifactFilter == null || resolvedArtifacts == null) {
artifacts = new LinkedHashSet<>();
} else {
artifacts = new LinkedHashSet<>(resolvedArtifacts.size() * 2);
for (Artifact artifact : resolvedArtifacts) {
if (artifactFilter.include(artifact)) {
artifacts.add(artifact);
}
}
}
}
return artifacts;
}
- maven又是如何获取到这些库文件的,相关代码如下:
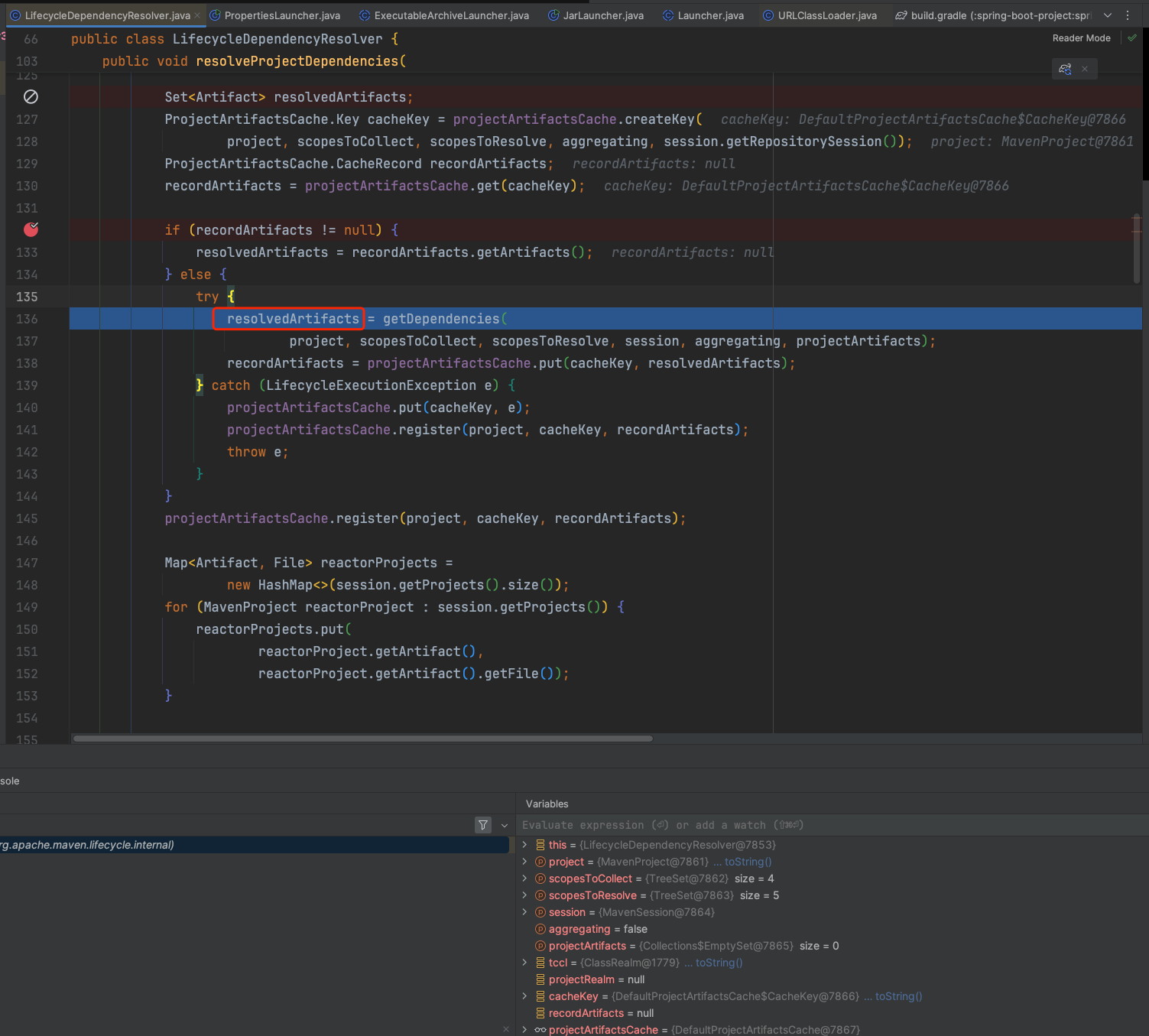
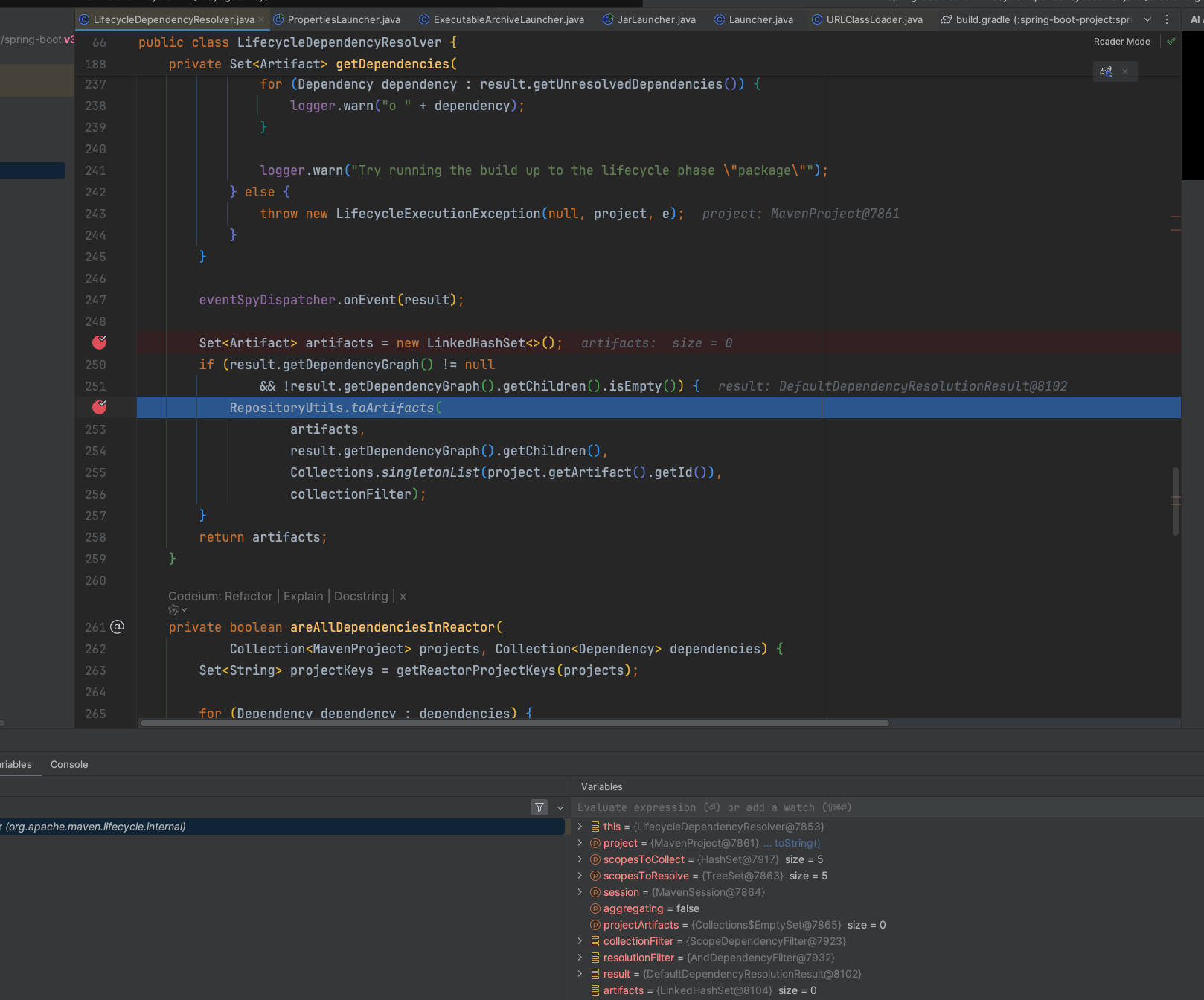
从toArtifacts代码分析,maven在解析依赖时,会遍历所有的直接依赖,然后把它们的依赖分别进行递归调用toArtifacts方法:
jar的顺序和pom中依赖的顺序一致
// RepositoryUtils
public static void toArtifacts(
Collection<org.apache.maven.artifact.Artifact> artifacts,
Collection<? extends DependencyNode> nodes,
List<String> trail,
DependencyFilter filter) {
for (DependencyNode node : nodes) {
org.apache.maven.artifact.Artifact artifact = toArtifact(node.getDependency());
List<String> nodeTrail = new ArrayList<>(trail.size() + 1);
nodeTrail.addAll(trail);
nodeTrail.add(artifact.getId());
if (filter == null || filter.accept(node, Collections.<DependencyNode>emptyList())) {
artifact.setDependencyTrail(nodeTrail);
artifacts.add(artifact);
}
toArtifacts(artifacts, node.getChildren(), nodeTrail, filter);
}
}
调试
准备
- 下载插件源码,IDEA导入
git clone https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot
# 切换需要调试的版本
git checkout v3.2.8
准备好测试项目,配置需要测试的插件 ,如spring-boot-maven-plugin,配置参考上方内容
两个项目JDK和Maven版本保持一致
执行
- 打断点
在源码项目中通过搜索@Mojo(name = "repackage"找到对应的核心类,在execute()方法打上断点

- 在测试项目控制台中执行
${maven_home}/mvnDebug clean package开启调试模式,等待IDEA连接,复制控制台输出的端口号
mvnDebug clean package

- 配置远程调试
在源码项目新建远程调试并且启动,端口为上一步复制的端口号,等待将进入断点